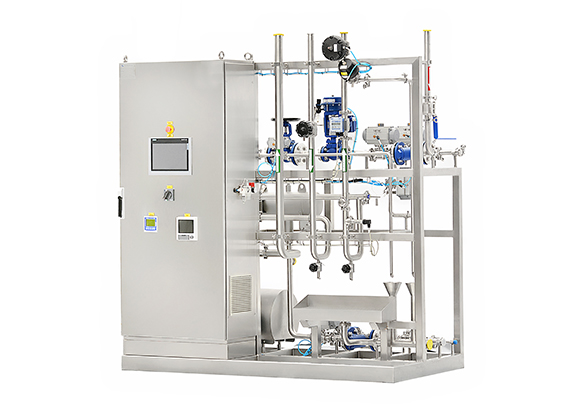
Product center




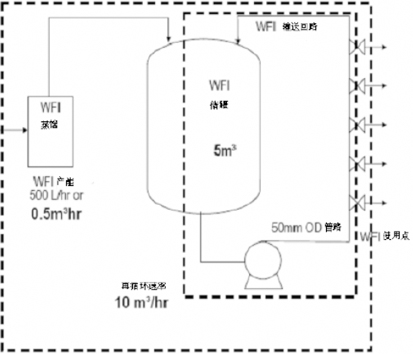
Distribution system
Design Concept
Control system
Process control
Process control
1.Using 3D modeling methods, modular design, reasonable pipeline layout, compact structure, reserved operating and maintenance space.
2.Automatically generate a material list with traceable specifications and models to avoid material shortage risks and ensure project progress.
3.Performing 3D model previews can identify risks in the early stages of a project, ensuring high predictability and flexibility during project execution. This ensures that the project meets optimal production operating standards, improves production efficiency, and simplifies production operations.
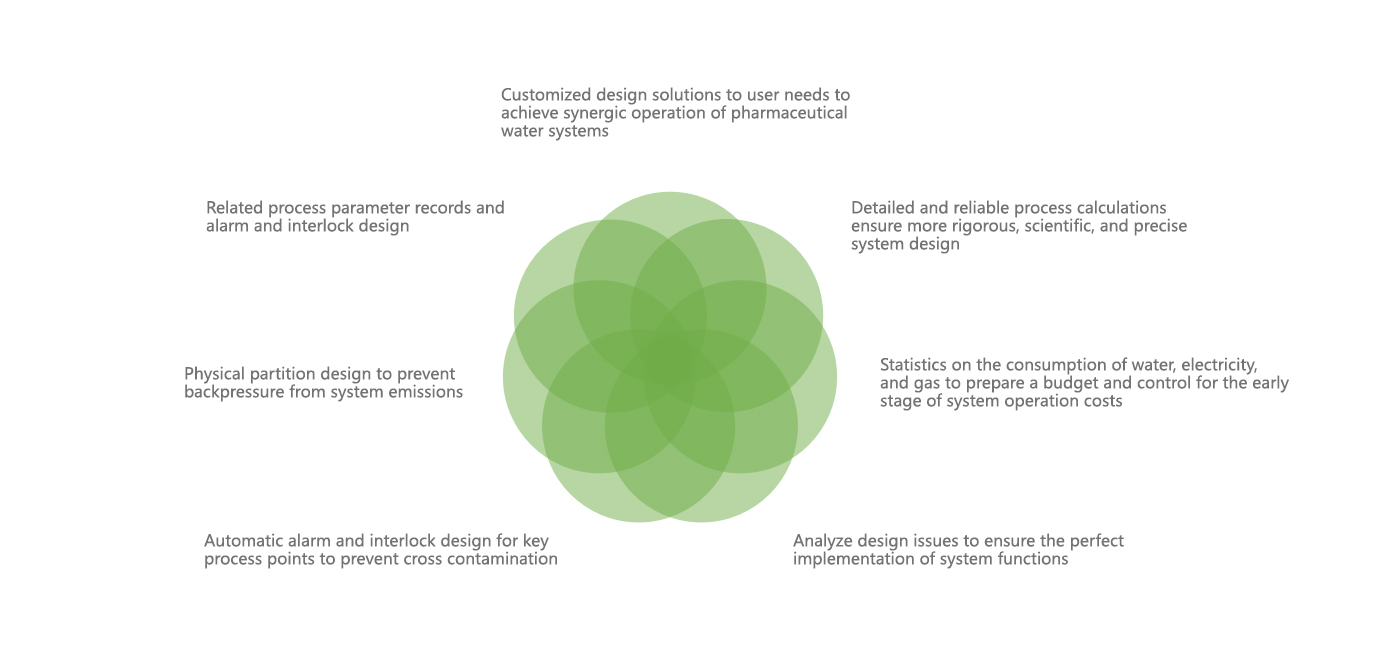
Implementation goals for pharmaceutical water systems
Realize the storage and distribution of pharmaceutical water. Minimize the microbial load of the system and the potential risk of contamination during operation. After running online for a certain period of time, the system can be thoroughly cleaned and sterilized to avoid the risk of cross contamination. The cleaning and sterilization process can be verified, the process temperature and time can be recorded, and the production process parameter data can be truly recorded and stored, printed, and traceable.
System engineering design
URS analysis
System plan
Microorganism control